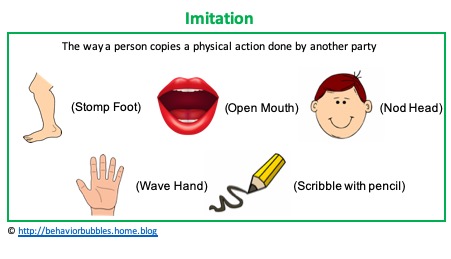
According to Cooper, Heron & Heward (2007), imitation is defined as a physical movement serving as a model with the behaviour occurring immediately (i.e. 3 to 5 seconds) following the model. Both the model and the behaviour must match the format shown (i.e. physical with physical, object with object). A learner can imitate a variety… Continue reading Imitation
Tag: ABA
Tact / Label
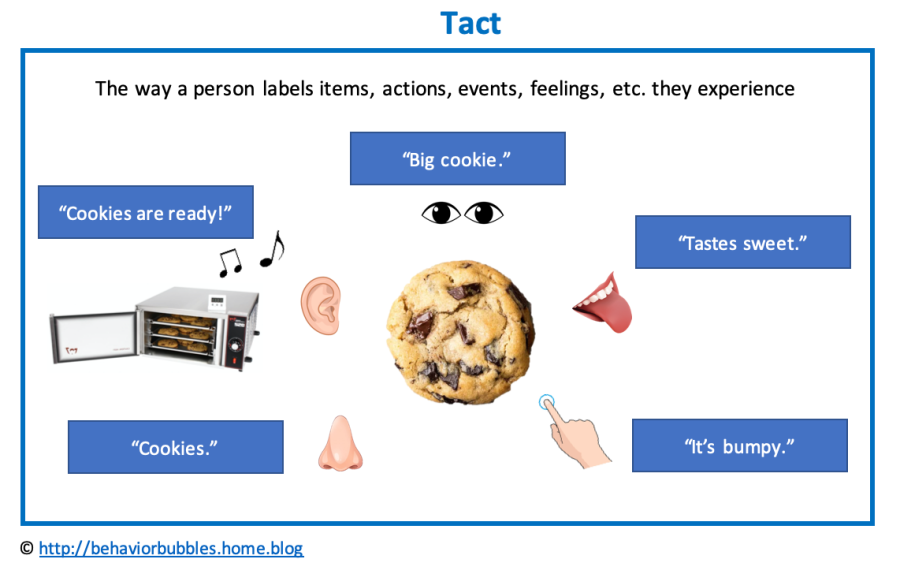
According to Cooper, Heron & Heward (2007), a “tact is a type of verbal operant in which a speaker names things and actions that the speaker has direct contact with through any of the sense modes.”. As such, a tact is a label that allows one to communicate and express themselves using language (e.g. learner… Continue reading Tact / Label
Verbal Operants
Some common terms used by ABA professionals consist of verbal operants. In this post, we will look at the following operants: Mand, Tact, Echoics, Intraverbals, Motor Imitation, & Listener Responding. MandThe learner making a request for something they want.Example: Should the learner want a cookie, they can Mand for the cookie by stating (1) “cookie”;… Continue reading Verbal Operants
Type of Reinforcers
Reinforcers are items or activities utilised to increase the future likelihood of behavior. Reinforcers fall into 2 domains. These would be ‘Primary Reinforcers’ and ‘Secondary Reinforcers’. Primary Reinforcers ‘aka’ Unconditioned ReinforcersThese serve as reinforcers naturally due to the biological needs of the learner (i.e. water, food, sleep, warmth, sex, etc.). Secondary Reinforcers ‘aka’ Conditioned ReinforcersThese… Continue reading Type of Reinforcers
Motivating Operation (MO)
Learning more about motivating operation (MO) is valuable for an instructor/parent to know. By understanding the underlaying concepts of MO, this helps the instructor/parent to understand why some behaviours might occur, and helps them to utilise reinforcers more effectively for the learner. What is Motivating Operation (MO)?According to Cooper, Heron, and Heward (2007), a motivating… Continue reading Motivating Operation (MO)
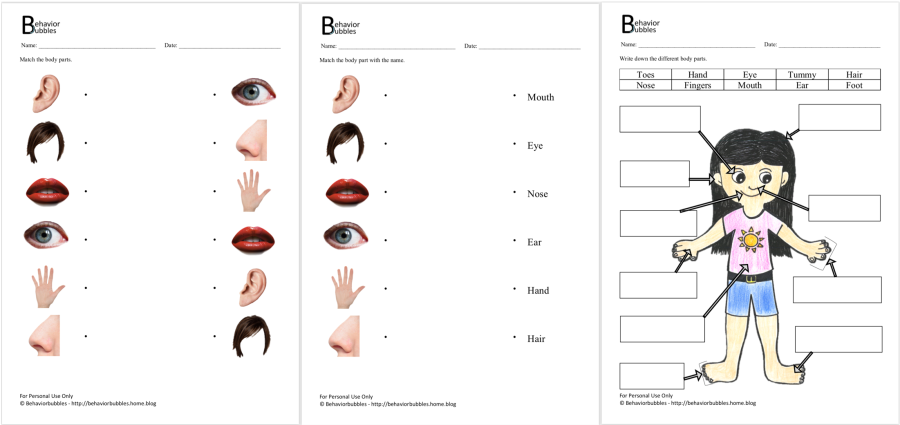
Body Parts
It is important to teach children body parts. It helps them to understand their body and forms an important basis for them to show or tell you where they might feel uncomfortable in future! Receptive Body PartsIn order to teach this skills, you can get the child to receptively identify body parts on themselves (i.e.… Continue reading Body Parts
Pronouns (He, She, His, Her)
A common issue parents and educators face is teaching pronouns (i.e. he, she, it, his, her, my, your, we, they, me, you, etc.). In today’s post, we will look at different ways to teach pronouns – specifically he, she, his, and her. Similar with other programs, you can teach pronouns utilising DTT (Discrete trial teaching)… Continue reading Pronouns (He, She, His, Her)
Function, Feature, Class
Function, feature, and class (FFC) is a skill that is prevalent in both the VBMAPP and ABLLS-R assessments. It serves as a way to teach a client that there is more to an item than its name and aids in future goals such as describing. There are many ways to teach this skill. Educators can… Continue reading Function, Feature, Class
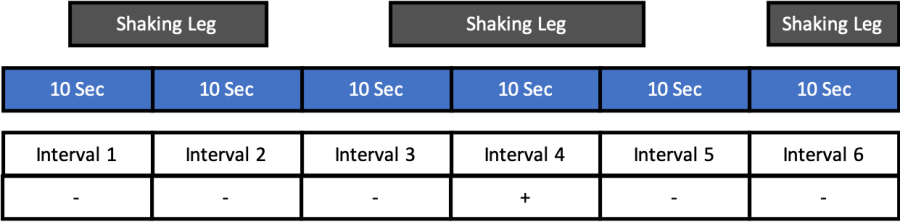
Discontinuous Measurement
Further to my previous post on continuous measurement (i.e. frequency, duration, latency, inter response time, etc.) which can be read here, I shall dive into discontinuous measurement today! Discontinuous measurement is defined as ‘measurement conducted in a manner such that some instances of the response class(es) of interest may not be detected’ (Cooper, Heron, &… Continue reading Discontinuous Measurement
Continuous Measurement
Knowing about types of continuous measurement is one of the requirements on the RBT competency assessment to become a Registered Behavior Technician (RBT). It is important to know the types of measurement as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is data driven. This implies that we rely on the data collected to gauge if a client is… Continue reading Continuous Measurement